The brake system is one of the most critical components of a vehicle, essential for ensuring the safety of the driver, passengers, and others on the road. Understanding how the brake system works can help you appreciate its importance and ensure it is properly maintained.
Components of the Brake System
The brake system is composed of several key components that work together to slow down and stop the vehicle:
- Brake Pedal:
- The driver applies force to the brake pedal to initiate braking.
- Master Cylinder:
- When the brake pedal is pressed, it activates the master cylinder, which converts the mechanical pressure from the pedal into hydraulic pressure.
- Brake Lines and Hoses:
- The hydraulic fluid is transmitted through brake lines and hoses to the brake calipers at each wheel.
- Brake Calipers:
- Brake calipers house the brake pads and use hydraulic pressure to press the pads against the brake rotors.
- Brake Pads:
- These friction materials press against the rotors to create the friction necessary to slow down the vehicle.
- Brake Rotors (Discs):
- Attached to the wheel hub, the rotors rotate with the wheels. When the brake pads clamp down on the rotors, friction is generated, slowing the wheel’s rotation.
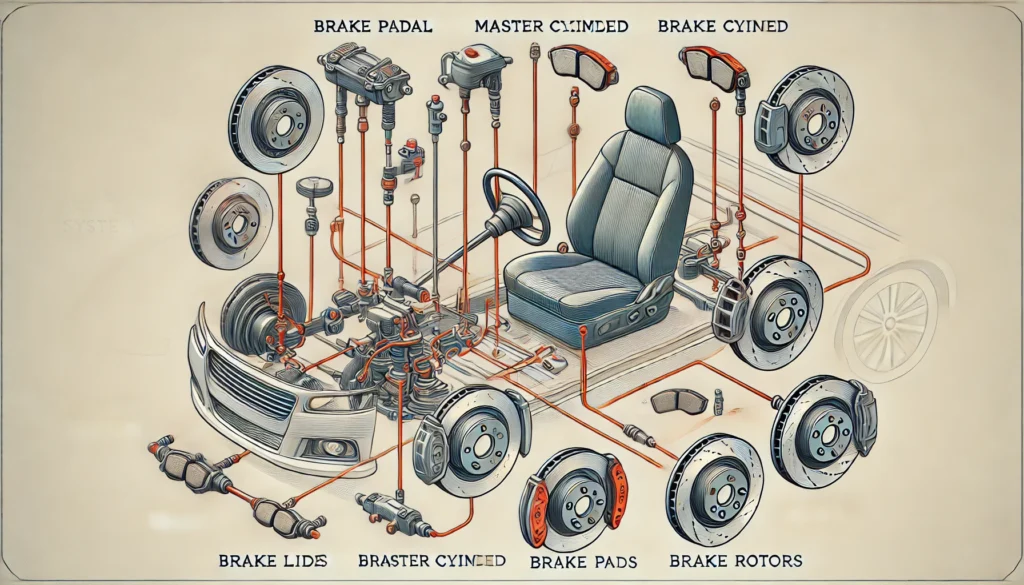
How the Brake System Works
Here is a step-by-step explanation of how the brake system operates:
- Pressing the Brake Pedal:
- The process begins when the driver presses the brake pedal. This action applies mechanical force to the master cylinder.
- Creating Hydraulic Pressure:
- The master cylinder converts the mechanical force into hydraulic pressure. This hydraulic pressure is then transmitted through the brake lines and hoses filled with brake fluid.
- Activating the Brake Calipers:
- The hydraulic pressure reaches the brake calipers at each wheel. The pressure forces the pistons within the calipers to move, causing the brake pads to press against the rotors.
- Generating Friction:
- The brake pads clamp down on the rotating brake rotors, creating friction. This friction is what slows down the rotation of the wheels, ultimately bringing the vehicle to a stop.
- Releasing the Brakes:
- When the driver releases the brake pedal, the hydraulic pressure is reduced. The brake pads retract slightly away from the rotors, allowing the wheels to spin freely again.
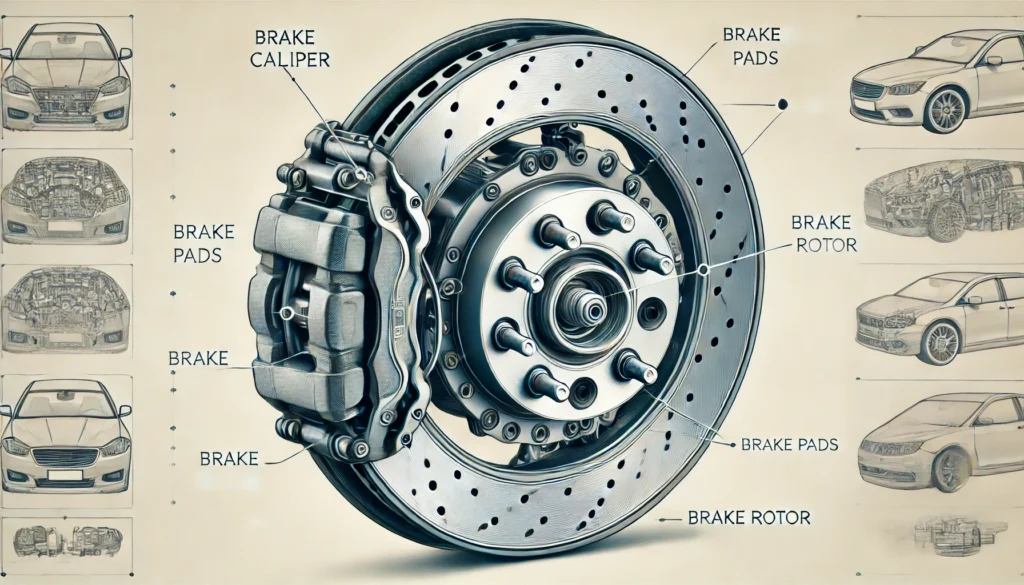
Types of Brake Systems
There are two main types of brake systems used in vehicles: disc brakes and drum brakes.
- Disc Brakes:
- Disc brakes use brake calipers, pads, and rotors to create friction. They are commonly found on the front wheels of most vehicles and are known for their superior stopping power and heat dissipation.
- Drum Brakes:
- Drum brakes use brake shoes that press against the inside of a drum attached to the wheel. They are typically found on the rear wheels of older or smaller vehicles. Drum brakes are less effective at heat dissipation compared to disc brakes.
Maintenance Tips for Brake Systems
To ensure your brake system functions properly, regular maintenance is essential:
- Check Brake Fluid:
- Regularly check the brake fluid level and top it up as needed. Replace the brake fluid according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Inspect Brake Pads and Rotors:
- Regularly inspect the brake pads for wear and replace them when necessary. Also, check the condition of the rotors and have them resurfaced or replaced if they are damaged.
- Monitor Brake Lines and Hoses:
- Inspect the brake lines and hoses for signs of leaks, cracks, or wear. Replace any damaged components immediately.
- Listen for Unusual Noises:
- Pay attention to any unusual noises when braking, such as squeaking or grinding. These sounds can indicate worn brake pads or other issues that need addressing.
Conclusion
The brake system is an integral part of vehicle safety, ensuring that the vehicle can slow down and stop effectively. Understanding how the brake system works and maintaining it properly can help you drive safely and avoid costly repairs. Regular inspections and timely replacements of worn components are crucial for the longevity and performance of your brake system.