The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) is a crucial safety feature in modern vehicles designed to prevent the wheels from locking up during braking. This system helps maintain steering control during emergency stops, reducing the risk of skidding and improving overall vehicle stability. Understanding how the ABS system works can help you appreciate its importance and ensure its proper maintenance.
Understanding the Components of ABS
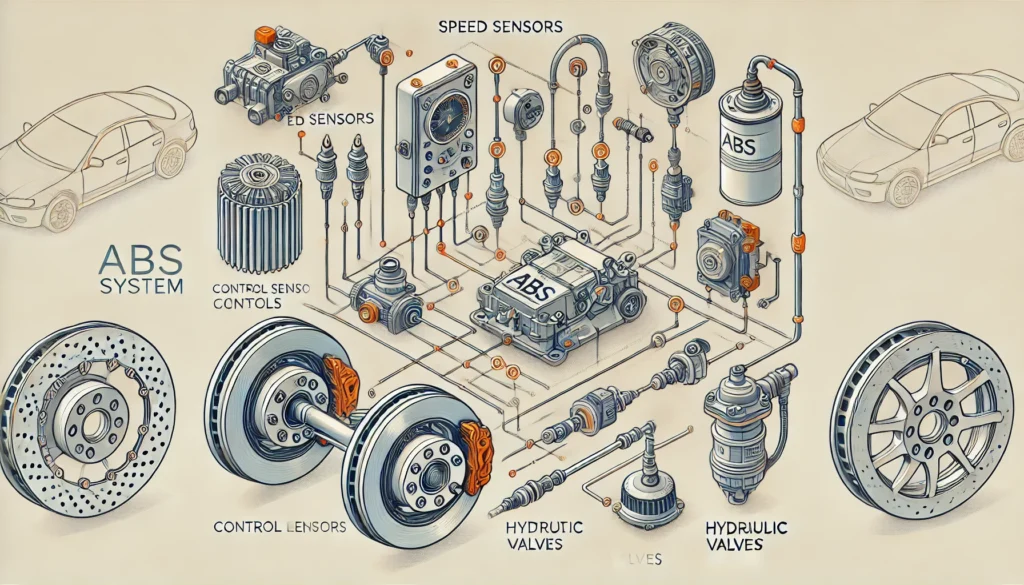
The ABS system consists of several key components that work together to prevent wheel lockup:
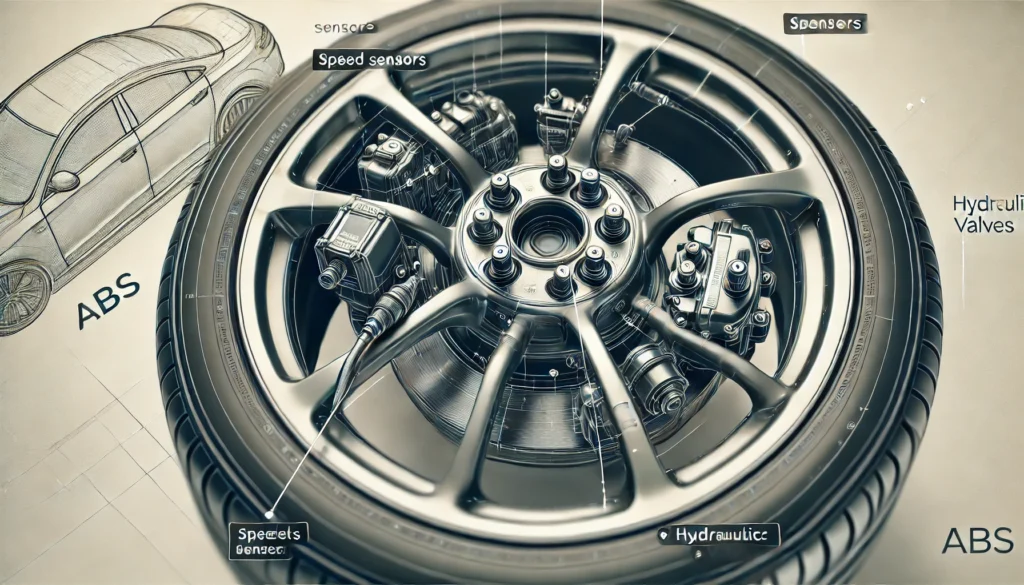
- Speed Sensors:
- These sensors are located at each wheel and monitor the wheel speed. They provide real-time data to the ABS control module.
- ABS Control Module:
- This is the brain of the ABS system. It processes the data from the speed sensors and determines when to activate the ABS.
- Hydraulic Valves:
- These valves are located in the brake lines of each wheel. The ABS control module controls them to regulate brake pressure.
- Pump:
- The pump restores the pressure to the hydraulic brakes after the ABS valves have released it.
How the ABS System Works
The ABS system works by rapidly modulating the brake pressure at each wheel to prevent them from locking up. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how the system operates:
- Normal Braking:
- During normal braking, the ABS system is inactive. The brake fluid flows from the master cylinder to the wheels without interference from the ABS.
- Detecting Lockup:
- When the driver applies the brakes heavily, the speed sensors at each wheel monitor the wheel speed. If a sensor detects that a wheel is decelerating too quickly and is about to lock up, it sends a signal to the ABS control module.
- Modulating Brake Pressure:
- The ABS control module processes the signal and activates the hydraulic valves for the affected wheel. These valves reduce the brake pressure by releasing some brake fluid, preventing the wheel from locking.
- Restoring Brake Pressure:
- Once the wheel regains traction, the ABS control module closes the valves, allowing the pump to restore brake pressure. This process repeats several times per second, ensuring that the wheels do not lock up while maintaining maximum braking efficiency.
- Driver Feedback:
- When the ABS is active, the driver may feel a pulsating sensation in the brake pedal. This is normal and indicates that the ABS is working correctly.
Benefits of ABS
The ABS system offers several benefits that enhance vehicle safety and performance:
- Improved Steering Control:
- By preventing wheel lockup, ABS allows the driver to maintain steering control during hard braking, which is critical for avoiding obstacles.
- Shorter Stopping Distances:
- On slippery surfaces, ABS can reduce stopping distances by preventing skidding and ensuring optimal brake pressure.
- Enhanced Vehicle Stability:
- ABS helps maintain vehicle stability during emergency braking, reducing the risk of losing control.
- Reduced Tire Wear:
- By preventing wheel lockup, ABS reduces flat-spotting and uneven tire wear, extending the life of the tires.
Maintenance Tips for ABS
To ensure the ABS system functions properly, regular maintenance is essential:
- Check Brake Fluid:
- Ensure the brake fluid is at the correct level and replace it as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Inspect Speed Sensors:
- Regularly inspect the speed sensors for dirt or damage and clean or replace them as needed.
- Monitor Brake Pads and Rotors:
- Check the condition of brake pads and rotors, replacing them if they are worn or damaged.
- Regular System Checks:
- Have a professional mechanic perform regular checks on the ABS system to ensure all components are functioning correctly.
Conclusion
The ABS system is a vital safety feature that enhances vehicle control and reduces the risk of accidents during emergency braking. Understanding how it works and maintaining it properly can help you stay safe on the road. Regular inspections and timely repairs will ensure your ABS system remains reliable and effective.